CRITICAL HEALTH INSURANCE

CRITICAL HEALTH INSURANCE
Serious illnesses such as cancer, heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and organ transplant not only affect physical health but also cause long-term financial instability. Rising hospital costs, income loss during recovery, and lifestyle adjustments can drain years of savings.
This is why critical illness insurance is becoming one of the most important components of modern financial planning. Unlike regular health insurance that reimburses hospitalization expenses, a critical illness insurance policy provides a lump sum payout on diagnosis, allowing individuals and families to manage treatment, recovery, and income gaps without financial stress.
In this detailed guide, you will learn:
- What critical illness insurance is
- How critical illness insurance works
- What diseases are covered and excluded
- Who should buy critical illness insurance
- How to choose the best critical illness insurance plan in India
What Is Critical Illness Insurance?
Critical illness insurance is a health protection policy that pays a fixed lump sum amount when the insured person is diagnosed with a listed life-threatening illness. The payout is independent of actual hospital expenses and can be used for any purpose, including treatment, home care, rehabilitation, loan repayments, or income replacement.
This makes critical illness insurance different from standard health insurance, which reimburses or cashless settles only medical bills.
How Does Critical Illness Insurance Work?
A critical illness insurance policy works by providing a lump sum payout when you are diagnosed with a covered serious illness. You first purchase a policy with a chosen sum insured such as ₹10 lakh, ₹25 lakh, or ₹50 lakh. If you are diagnosed with a listed critical condition, you submit the required medical documents, and after the survival period, the insurer pays the full coverage amount. In most policies, coverage ends after the claim, although some plans allow multiple claims across different illnesses. This structure makes critical illness insurance a powerful tool for income protection and financial stability during medical emergencies.
Diseases Covered Under Critical Illness Insurance
Most critical illness insurance plans in India offer coverage for a wide range of serious and life-threatening medical conditions, usually between 15 and 40 major diseases, depending on the insurer and policy type. These typically include major-stage cancers, heart attack (myocardial infarction), stroke, coronary artery bypass graft surgery (CABG), kidney failure requiring regular dialysis or transplant, and major organ transplants. Many policies also cover permanent paralysis, multiple sclerosis, aorta surgery, coma, and severe burns. Since treatment for these conditions often involves long-term care, high medical costs, and loss of income, this coverage plays a crucial role in providing financial stability during recovery. However, the exact list of illnesses and their definitions vary across insurers, so it is essential to carefully review the policy wording before purchasing.
The exact list and definitions vary across insurers, so it is important to review the policy document carefully before purchasing.
What Is Not Covered Under Critical Illness Insurance?
Understanding exclusions is essential to avoid claim rejection and ensure smooth settlement under a critical illness insurance policy. Common exclusions include early-stage or non-invasive cancers, pre-existing illnesses during the waiting period, congenital disorders, self-inflicted injuries, conditions not specifically listed in the policy wording, and illnesses arising from alcohol or substance abuse. Since coverage depends heavily on medical definitions and policy terms, it is important to carefully review waiting periods, survival clauses, and disease definitions before purchasing to ensure full eligibility at the time of claim.
Critical Illness Insurance vs Health Insurance: Key Differences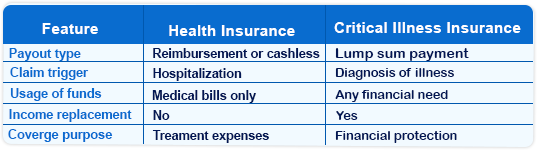
Who Should Buy Critical Illness Insurance?
Critical illness insurance is highly recommended for salaried professionals, self-employed individuals, and primary income earners who want to protect their financial stability in case of a serious medical diagnosis. It is especially important for people with a family history of critical illnesses, those with financial dependents, and individuals who do not have large emergency savings to manage long-term treatment and recovery costs. Even young adults benefit from buying critical illness insurance early, as premiums are lower, eligibility is broader, and coverage can be secured before health conditions develop.
Benefits of Critical Illness Insurance
1. Lump Sum Financial Support
The insured receives the entire coverage amount at once, offering immediate financial relief during diagnosis.
2. Income Replacement During Recovery
Long recovery periods often cause loss of income. Critical illness insurance helps maintain financial stability.
3. Coverage for Non-Medical Expenses
Expenses such as travel, home nursing, lifestyle changes, and rehabilitation are covered.
4. Affordable Premiums for High Coverage
Critical illness insurance offers significant coverage at comparatively low premiums.
5. Mental and Financial Peace of Mind
Knowing your finances are protected allows complete focus on recovery.
How Much Critical Illness Coverage Do You Need?
The amount of critical illness insurance you need should be carefully assessed to provide adequate financial protection in case of a major health diagnosis. A well-planned coverage ensures that medical costs, income loss, and long-term financial responsibilities are managed without stress. Your coverage requirement depends on
• Annual income
• Number of dependents
• Current health insurance coverage
• Existing savings and liabilities
• Lifestyle risks and family medical history
Recommended coverage:
3 to 5 times your annual income.
Example:
If your annual income is ₹10 lakh, your ideal critical illness cover should range between ₹30 lakh and ₹50 lakh.
How to Choose the Best Critical Illness Insurance Plan in India
When selecting the best critical illness insurance policy, consider the following:
1. Number of Diseases Covered
Choose policies covering at least 20 to 30 major illnesses.
2. Claim Settlement Ratio
Higher ratios indicate better claim performance and reliability.
3. Waiting Period and Survival Period
Shorter periods improve claim eligibility.
4. Policy Terms and Renewability
Prefer lifelong renewability and long-term coverage.
5. Standalone Policy vs Rider
Standalone critical illness insurance plans provide better illness definitions, higher sums insured, and broader coverage compared to riders.
Standalone Critical Illness Insurance vs Critical Illness Rider
Feature | Standalone Policy | Rider |
Sum insured | Higher | Limited |
Illness definitions | Detailed | Restricted |
Policy flexibility | High | Low |
Claim usability | Broad | Limited |
If your goal is serious financial protection, standalone critical illness insurance is the superior option.
Common Mistakes to Avoid While Buying Critical Illness Insurance
Many policyholders make avoidable errors while purchasing critical illness insurance, which can later lead to claim rejection or inadequate coverage. Being aware of these mistakes helps in choosing the right policy and ensuring smooth claim settlement. Common mistakes include:
• Choosing insufficient coverage
• Ignoring illness definitions
• Overlooking survival and waiting periods
• Relying only on employer-provided health insurance
• Not disclosing medical history
• Selecting policies based on premium alone
Avoiding these mistakes significantly reduces the risk of claim rejection and ensures better financial protection.
Is Critical Illness Insurance Worth Buying?
Yes. With rising medical inflation, increasing lifestyle diseases, and unpredictable health risks, critical illness insurance provides financial stability when income and expenses are most vulnerable.
While health insurance covers treatment costs, critical illness insurance protects your income, savings, and lifestyle.
Final Thoughts
Critical illness impacts not just health, but income, career, family responsibilities, and future plans. A well-chosen critical illness insurance policy ensures that financial stress does not interrupt your recovery.
The earlier you buy, the lower your premium and the broader your coverage eligibility. Delaying increases both financial and medical risk exposure.

